BY Simmi Kava
JavaScript: Optional Chaining Operator (?.)
Optional Chaining Operator (?.)
This operator allows you to read the value of property situated deep within a chain of connected objected without the need to check if each reference in the chain is valid or not.
Difference between ?. and . chaining operator
. chaining operator throws an error if a reference is null or undefined.
?. will return undefined if a reference is null or undefined.
The optional chaining operator comes handy when you are evaluating an object and unsure which all properties of the object are required.
Can we use ?. on undefined root object?
Yes
Can we use ?. on root object which is not declared?
No
Syntax
obj.val?.prop
obj.val?.[expr]
obj.arr?.[index]
obj.func?.(args)
Examples
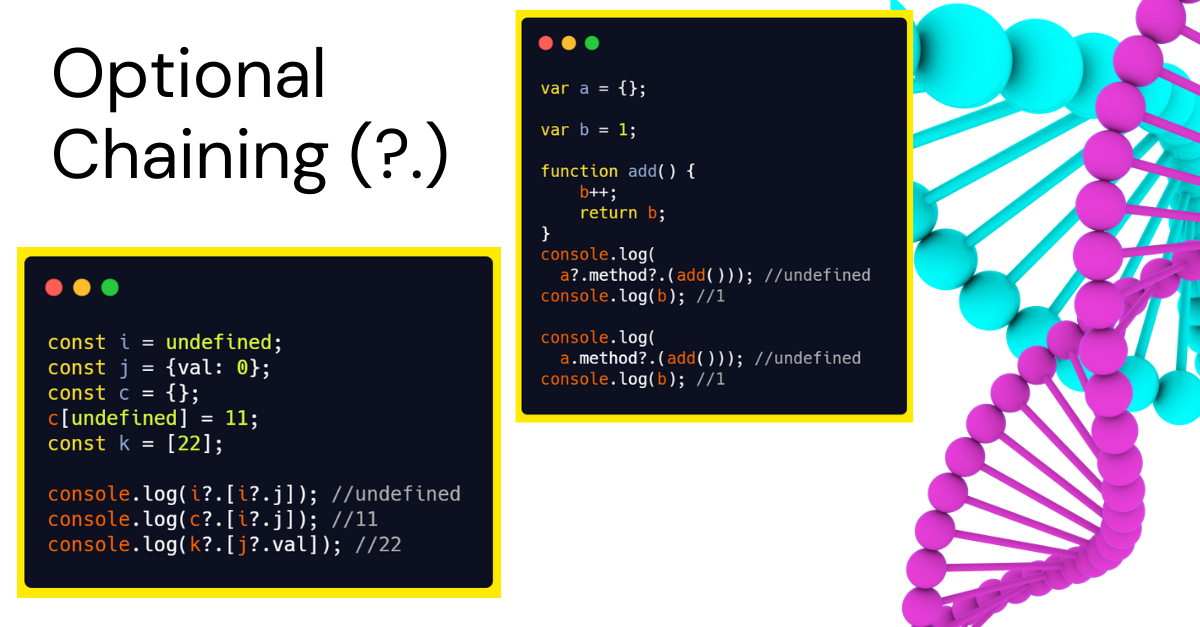
const i = undefined;
const j = {val: 0};
const c = {};
c[undefined] = 11;
const k = [22];
console.log(i?.[i?.j]); //undefined
console.log(c?.[i?.j]); //11
console.log(k?.[j?.val]); //22
Optional Chaining - Method Call Example
var a = {};
var b = 1;
function add() {
b++;
return b;
}
console.log(a?.method?.(add())); //undefined
console.log(b); //1
console.log(a.method?.(add())); //undefined
console.log(b); //1
Optional Chaining Index Example
var a = null;
var b = 1;
function add() {
b++;
return b;
}
var n = a?.[add()];
console.log(n); //undefined
console.log(b); //1
Keep Learning!
BY Simmi Kava
 |  |  |  |
| Like | Comment | Save | Share |
ARCHIVES
2025
2024
2023
2022
/api/attachments/att/4/linkedin-null-nan-1200-628.png/linkedin-null-nan-1200-628.100.jpg)
/api/attachments/att/249/webP.gif/webP.100.jpg)
